ABSTRACT
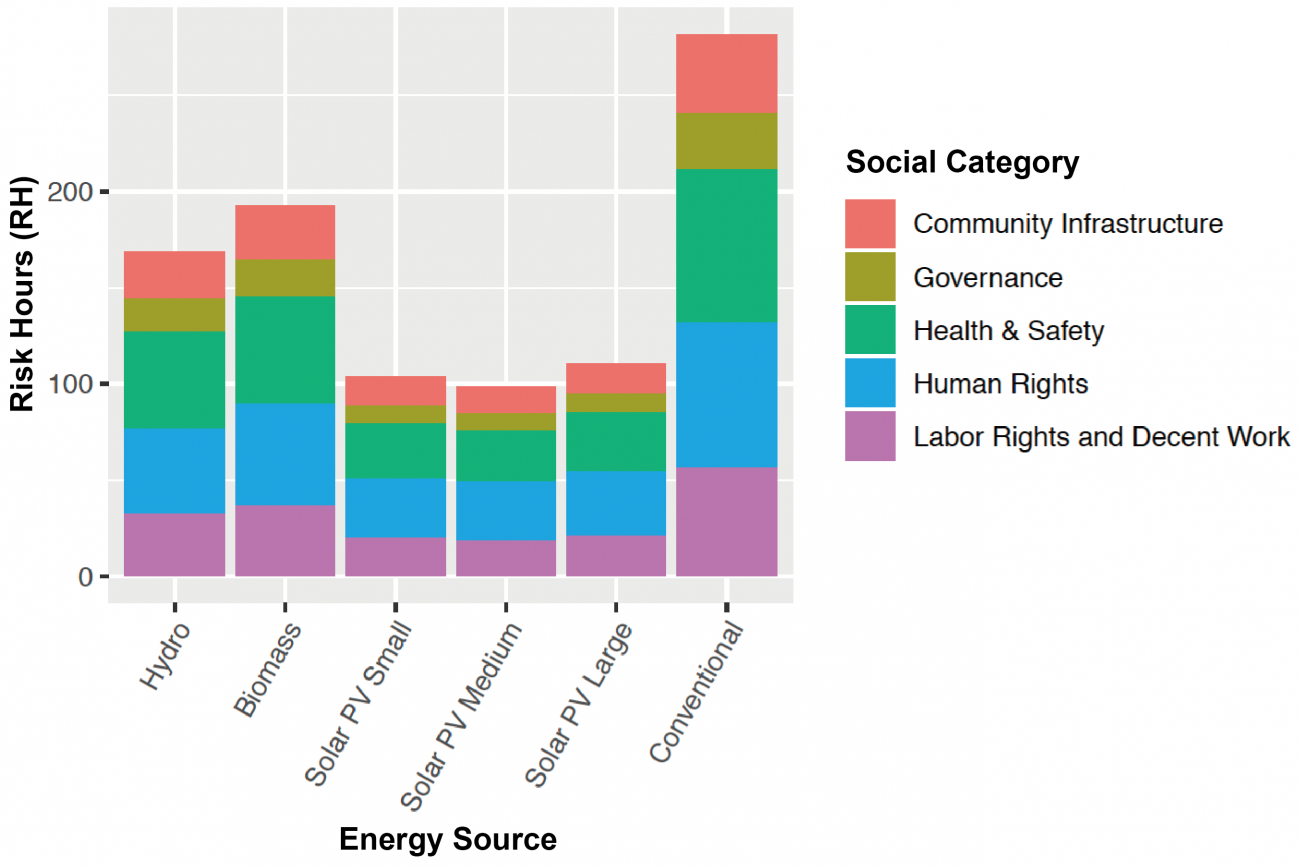
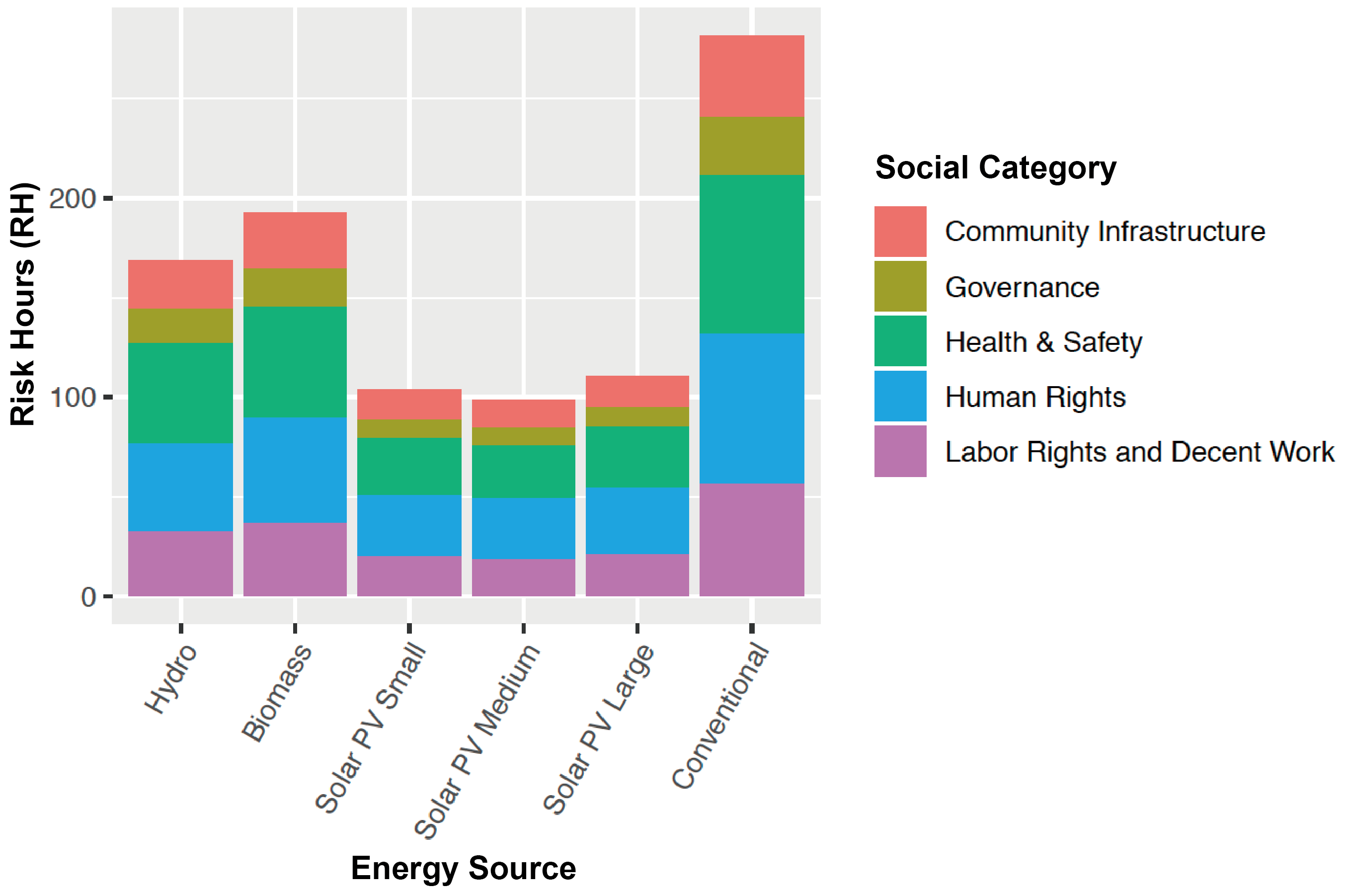
The adoption of renewable energy technologies in developing nations is recognized to have positive environmental impacts; however, what are their effects on the electricity supply chain workers? This article provides a quantitative analysis on this question through a relatively new framework called social life cycle assessment, taking Malaysia as a case example. Impact assessments by the authors show that electricity from renewables has greater adverse impacts on supply chain workers than the conventional electricity mix: Electricity production with biomass requires 127% longer labor hours per unit-electricity under the risk of human rights violations, while the solar photovoltaic requires 95% longer labor hours per unit-electricity. However, our assessment also indicates that renewables have less impacts per dollar-spent. In fact, the impact of solar photovoltaic would be 60% less than the conventional mix when it attains grid parity. The answer of “are renewables as friendly to humans as to the environment?” is “not-yet, but eventually.
JOURNAL
Sustainability 2019, 11(5), 1370